-
Research Article
-
Noise Analysis of Resistivity Data at a Dam
댐에서 얻어진 전기비저항 탐사 자료의 잡음 분석
-
Keun-Soo Lee, Ki-Ju Kim, Myung-Jin Ha, Ki-Seog Kim, Nam-Hyun Lee, and In-Ky Cho
이근수, 김기주, 하명진, 김기석, 이남현, 조인기
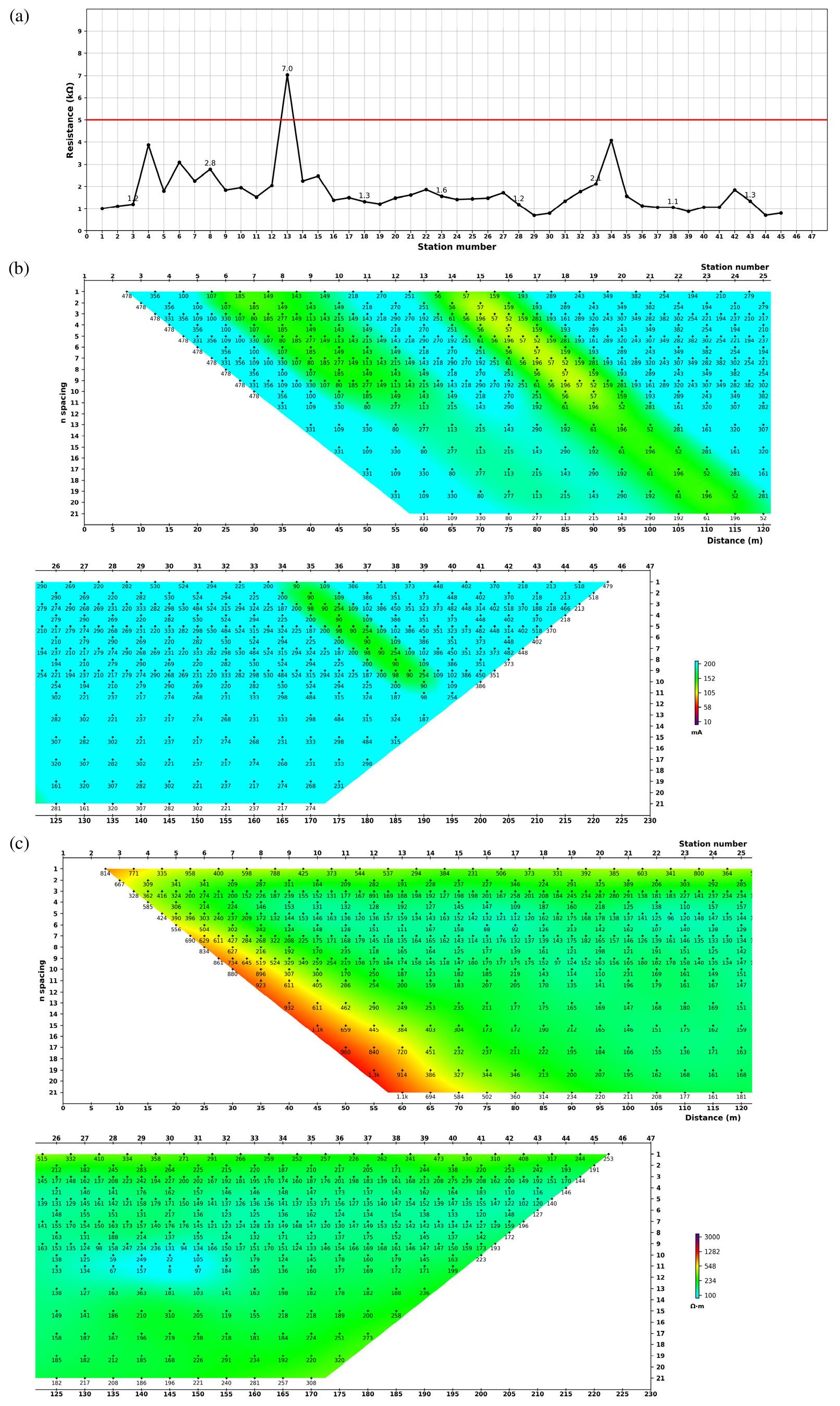
- For a more accurate interpretation of resistivity data, noise must be properly understood and quantified as much as possible. Because measurement errors …
전기비저항 탐사 자료의 더 정확한 해석을 위해서는 잡음을 정확하게 이해하고 가능하면 정량화해야 한다. 측정 오차는 전기비저항 탐사자료의 역산에서 중요하다. 신뢰도가 높고 현실적인 …
- For a more accurate interpretation of resistivity data, noise must be properly understood and quantified as much as possible. Because measurement errors can play a pivotal role in the inversion, accurate specification of measurement errors is essential to obtain reliable, realistic inversion results. As a preliminary study to develop an effective method quantifying measurement errors, stacking and reciprocal errors were compared for their utility in describing measurement errors. For two resistivity datasets measured at a relatively noisy dam site, the relationships among the contact resistance, injection current, apparent resistivity, stacking error, and reciprocal error were analyzed. The results shows that the measurement error is significantly influenced by contact resistance and that the reciprocal error provides a good estimate of the measurement error. In contrast, the stacking error tends to underestimate the noise level.
- COLLAPSE
전기비저항 탐사 자료의 더 정확한 해석을 위해서는 잡음을 정확하게 이해하고 가능하면 정량화해야 한다. 측정 오차는 전기비저항 탐사자료의 역산에서 중요하다. 신뢰도가 높고 현실적인 역산 결과 영상을 얻으려면 측정 오차를 정확하게 예측하는 것이 중요하다. 측정 오차를 정량화하는 효과적인 방법을 개발하기 위한 예비 연구로서, 중합오차와 상반성오차를 측정 오차를 비교하였다. 비교적 잡음수준이 높을 것으로 예상되는 댐에서 측정된 두 전기비저항 탐사 자료에 대해 접촉 저항, 주입 전류, 겉보기 전기비저항, 중합오차, 그리고 상반성오차들 사이의 관계를 분석하였다. 분석 결과 측정 오차는 접촉 저항에 크게 영향을 받으며, 상반성오차는 측정 잡음을 적정하게 평가하는 반면, 중합오차는 저평가하는 경향을 나타내었다.
-
Noise Analysis of Resistivity Data at a Dam
-
Research Article
-
Selecting of an Optimal Borehole Location for Magnetic Exploration Based on Joint Inversion of Multispacing Magnetic Data
다중 공간 자력 자료 복합 역산을 이용한 최적의 자력 탐사 시추공 위치 선정
-
Gyeongnoh Kim, Gyesoon Park, and Hyoungrea Rim
김경노, 박계순, 임형래
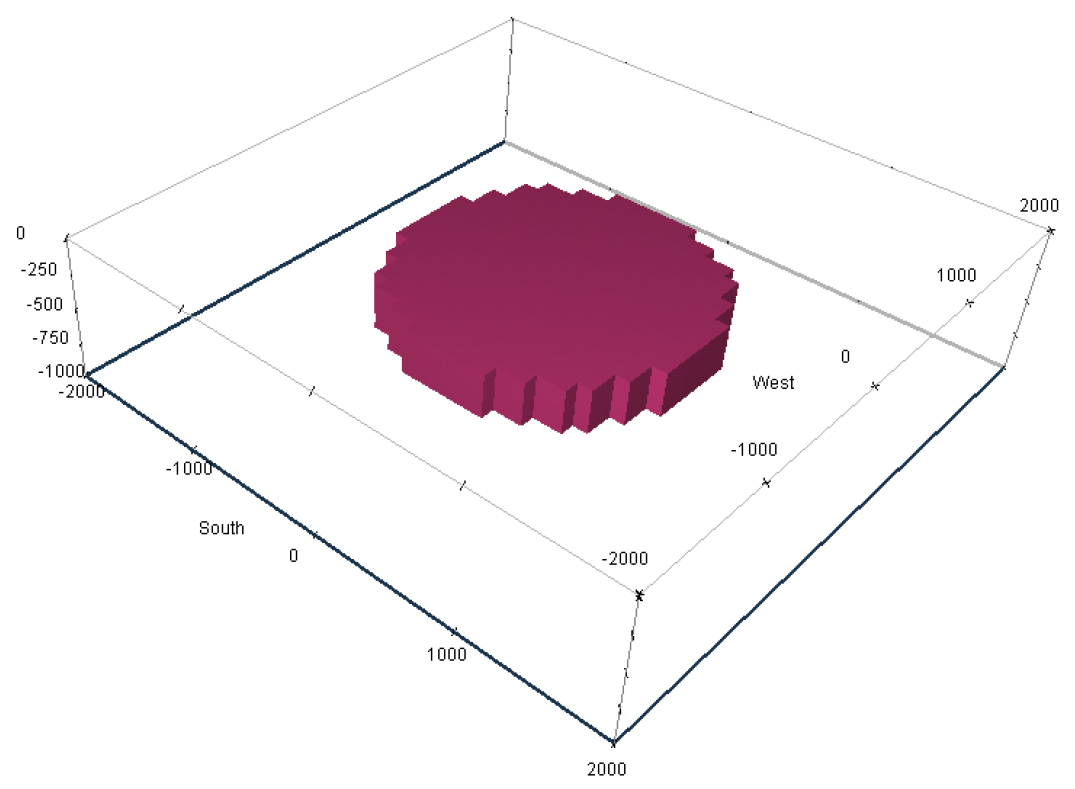
- This study proposes an optimal borehole location through the joint inversion of multiple spatial magnetic datasets, comprising ground-based magnetic data and single-borehole …
이 논문에서는 지표와 단일 시추공에서 획득한 다중 공간 자력 자료를 복합 역산하여 최적의 시추공 위치를 제안하였다. 시추공의 위치에 따른 역산 성능의 차이를 …
- This study proposes an optimal borehole location through the joint inversion of multiple spatial magnetic datasets, comprising ground-based magnetic data and single-borehole magnetic measurements. A horizontal disk model was introduced to systematically investigate the effect of borehole location on inversion performance. To quantitatively assess the accuracy of the inversion results, the target boundary was determined using the method proposed by Otsu (1979). The similarities between the inverted and true disk models were quantitatively evaluated by employing a confusion matrix-based analysis. The quantitative joint inversion analysis, which systematically incorporates variations in borehole location, geomagnetic declination, and inclination angles demonstrates that the optimal borehole configuration for magnetic exploration in the Northern Hemisphere is attained when the borehole azimuth is precisely aligned with the geomagnetic declination direction. This result provides a practical criterion for borehole placement in field applications, in which the number of boreholes is often constrained by economic factors. Therefore, the proposed approach is expected to enhance the efficiency of magnetic anomaly detection in practical field environments.
- COLLAPSE
이 논문에서는 지표와 단일 시추공에서 획득한 다중 공간 자력 자료를 복합 역산하여 최적의 시추공 위치를 제안하였다. 시추공의 위치에 따른 역산 성능의 차이를 분석하기 위해 수평 원판형 이상체를 도입하였다. 역산 결과의 정확도를 정량적으로 분석하기 위하여 Otsu (1979)가 제안한 기법에 기초하여 이상체의 경계를 설정하였다. 역산 결과로 복원된 이상체 영역과 원판 이상체 모델의 이상체 영역 간의 유사도를 혼동 행렬 (confusion matrix)을 이용하여 정량적으로 계산하여 비교하였다. 시추공 위치와 지자기장의 편각 및 복각 변화에 따른 정량적 복합 역산 결과에 따르면, 북반구에서 자력 탐사를 위한 최적의 시추공 위치는 시추공 방위각이 지자기장 편각과 일치할 때로 확인되었다. 이러한 연구 결과는 실제 자력 탐사 현장에서 탐사 비용 등의 문제로 시추공의 수를 제한하고자 할 때, 최적의 위치를 선정함에 있어 직접적인 근거 자료로 활용될 수 있다. 또한 이 과정에서 자력 탐사를 통해 자기 이상체의 탐지 효율을 향상시킬 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
-
Selecting of an Optimal Borehole Location for Magnetic Exploration Based on Joint Inversion of Multispacing Magnetic Data
-
Research Article

-
A Case Study of Noise Source Analysis Using an Onboard Quality Control System in Streamer Seismic Surveys
선상 품질관리 시스템을 활용한 스트리머 탐사의 잡음원 분석 사례
-
Dowan Kim, Donghoon Lee, Sooyoon Kim, Bo-Yeon Yi, Junseok Kwon, Yonghwan Joo, and Moohee Kang
김도완, 이동훈, 김수윤, 이보연, 권준석, 주용환, 강무희
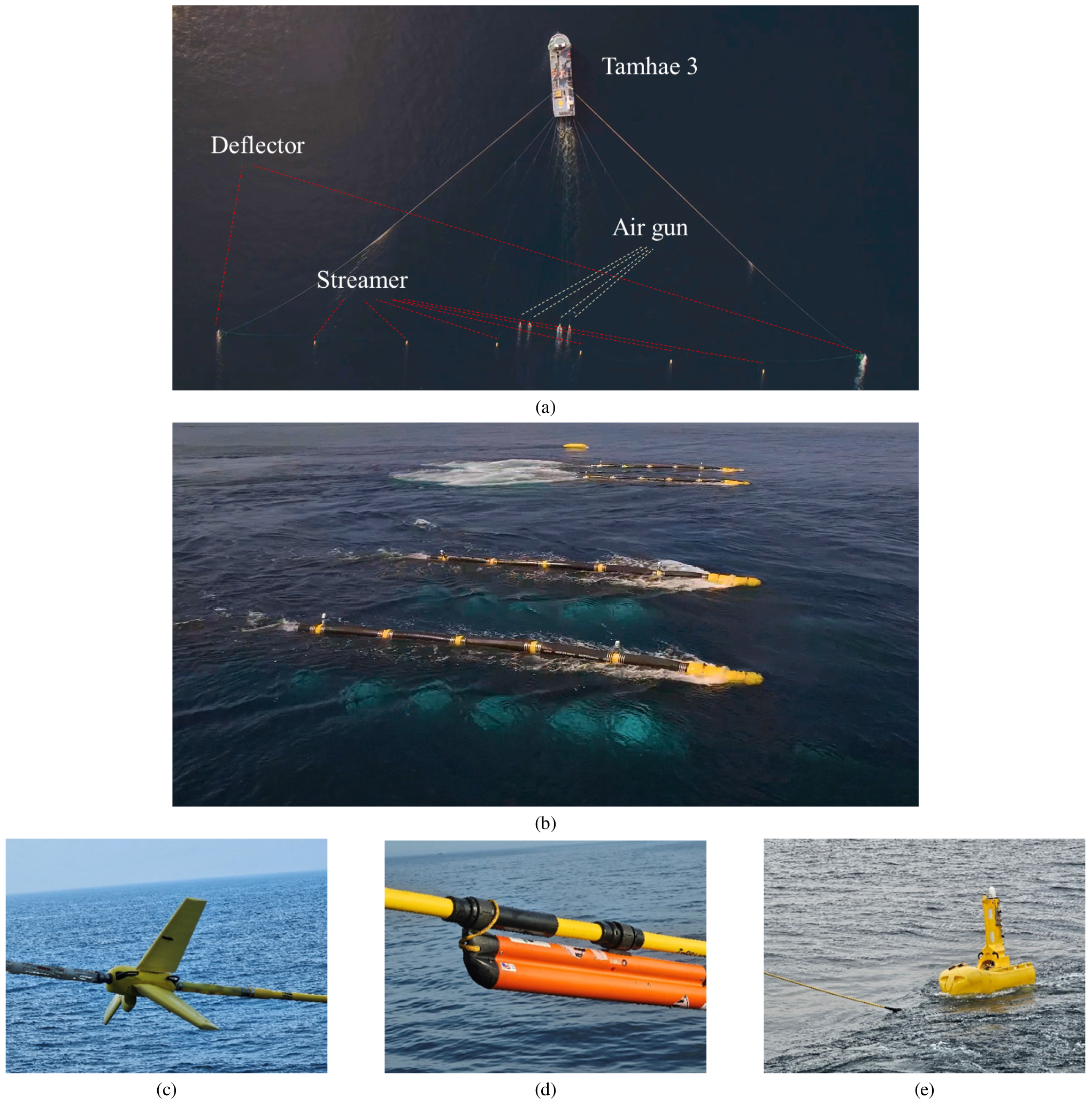
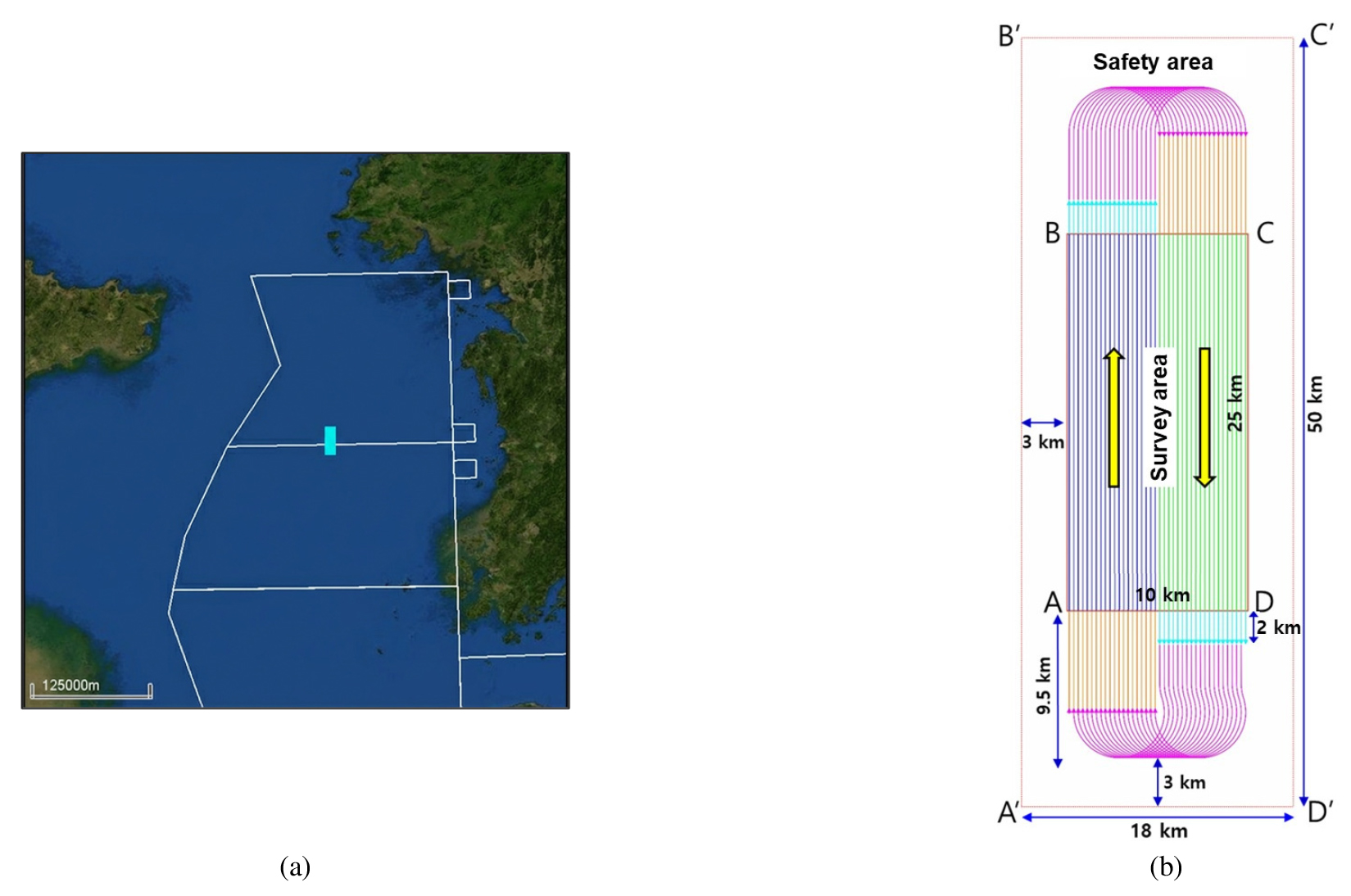
- Marine seismic surveys are applied to investigate subseafloor geological structures and to explore natural resources. In particular, streamer-based surveys are widely applied …
해양 탄성파 탐사는 해저 지질 구조를 규명하고 천연자원 탐사를 위한 기초 자료를 확보하는 데 필수적인 기술이다. 특히 스트리머를 이용한 해양 탄성파 탐사는 …
- Marine seismic surveys are applied to investigate subseafloor geological structures and to explore natural resources. In particular, streamer-based surveys are widely applied in oil and gas exploration and in marine geological investigations and carbon capture and storage (CCS) site assessments. In such surveys, data quality can significantly affect the success of the exploration, making onboard quality control (QC) essential for detecting anomalies early. Diverse noise sources are present in Korean waters due to active fishing activities and frequent environmental changes. Therefore, it is important to establish a system that goes beyond basic equipment operation and enables accurate identification of noise types and appropriate countermeasures. In May 2024, the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) launched its new research vessel, Tamhae 3, and has since been developing and advancing an onboard QC system. This study presents the application of the QC system onboard Tamhae 3 seismic surveys. It also classifies major noise sources observed during the survey and examines their impacts on seismic data with field examples.
- COLLAPSE
해양 탄성파 탐사는 해저 지질 구조를 규명하고 천연자원 탐사를 위한 기초 자료를 확보하는 데 필수적인 기술이다. 특히 스트리머를 이용한 해양 탄성파 탐사는 석유·가스 자원 탐사뿐만 아니라 해양 지질조사, 이산화탄소 저장소 탐색 등 다양한 분야에 활용되고 있다. 이러한 해양 탐사에서는 자료 품질이 탐사의 성패를 좌우할 수 있기 때문에, 실시간으로 탐사 상태를 점검하고 이상 징후를 조기에 식별할 수 있는 선상 품질관리가 필수적이다. 특히 어업 활동이 활발하고 탐사 환경 변화가 큰 한반도 인근 해역에서는 다양한 형태의 잡음원이 존재하며, 이는 탐사 자료의 품질에 직접적인 영향을 미칠 수 있다. 따라서 단순한 장비 운용을 넘어, 잡음의 유형을 식별하여 이에 대응할 수 있어야 한다. 한국지질자원연구원은 2024년 5월, 6,900톤급 신규 물리탐사연구선 ‘탐해3호’의 공식 취항을 계기로, 선상 품질관리 시스템을 구축하였으며 지속적인 고도화를 추진하고 있다. 본 논문에서는 국내외 해역에서 수행된 스트리머 탐사를 대상으로, 탐해3호 선상에서 적용된 품질관리 시스템과 그 운용 방법을 기술하였다. 또한 탐사 중 관측된 주요 잡음원들의 유형과 이들이 탐사 자료에 미친 영향을 정리하였다.
-
A Case Study of Noise Source Analysis Using an Onboard Quality Control System in Streamer Seismic Surveys
-
Research Article
-
A Time-Domain Processing and Quality-Control Workflow for 3D Marine Seismic Data in the Shallow Waters of the Yellow Sea
서해 천해 3차원 탄성파 자료의 시간 영역 처리 흐름도 및 품질관리 사례
-
Sooyoon Kim, Moohee Kang, Yonghwan Joo, Donghoon Lee, Dowan Kim, and Joonyoung Kwak
김수윤, 강무희, 주용환, 이동훈, 김도완, 곽준영
- This study presents a time-domain processing case for a three-dimensional (3D) marine seismic dataset acquired on the shallow continental shelf of the …
서해 얕은 해역 대륙붕에서 탐해 3호의 최신 물리탐사 장비를 이용해 취득된 첫 3차원 탄성파 탐사 자료에 대한 시간 영역 처리 사례를 제시하였다. …
- This study presents a time-domain processing case for a three-dimensional (3D) marine seismic dataset acquired on the shallow continental shelf of the western offshore Korea (Yellow Sea) using KIGAM’s research vessel Tamhae-3. The raw data were significantly degraded by complex marine noise and strong multiples inherent to shallow-water environments. Through a stepwise application of tailored noise and multiple attenuation techniques, the quality of the final stack section was substantially improved, enabling successful imaging of the acoustic basement boundary. Based on this field data, we establish a time-domain seismic processing workflow comprising a series of processing and quality-control steps and evaluate the effectiveness of each processing stage. The results provide a practical case study and methodological reference for 3D seismic data processing and quality-control procedures in shallow-water environments. These are expected to contribute to future processing efforts under similar geological and acquisition conditions.
- COLLAPSE
서해 얕은 해역 대륙붕에서 탐해 3호의 최신 물리탐사 장비를 이용해 취득된 첫 3차원 탄성파 탐사 자료에 대한 시간 영역 처리 사례를 제시하였다. 이 해역에서 취득된 자료는 복잡한 해양 잡음과 강한 다중반사파로 원시 신호의 품질이 저하된 상태였다. 단계적으로 맞춤형 잡음 감쇄와 다중반사파 제거 기법들을 적용한 결과 최종 중합 단면의 신호 품질이 크게 개선되었으며, 목표 심도인 심부 기반암 경계까지 명확히 영상화되었다. 본 사례 연구를 통해 전체 시간 영역 자료처리 흐름도와 품질관리 기준을 제시하고, 각 처리 단계에서의 효과를 현장 자료를 기반으로 검증하였다. 이러한 연구 결과는 대륙붕 환경에서의 3차원 탄성파 자료처리 절차와 품질관리 기법에 대한 구체적인 사례를 제공함으로써 향후 유사 환경 자료처리의 유용한 방법론적 참고자료가 될 것으로 기대된다.
-
A Time-Domain Processing and Quality-Control Workflow for 3D Marine Seismic Data in the Shallow Waters of the Yellow Sea
-
Research Article
-
A Prestack Impedance Inversion for CCS Candidate Site Without a Well: A Case Study of Gunsan Basin
시추공이 부재한 CCS 후보지역에서의 중합전 임피던스 역산: 서해 군산분지 사례 연구
-
Jwagyum Kim, Soon Jee Seol, and Joongmoo Byun
김좌겸, 설순지, 변중무
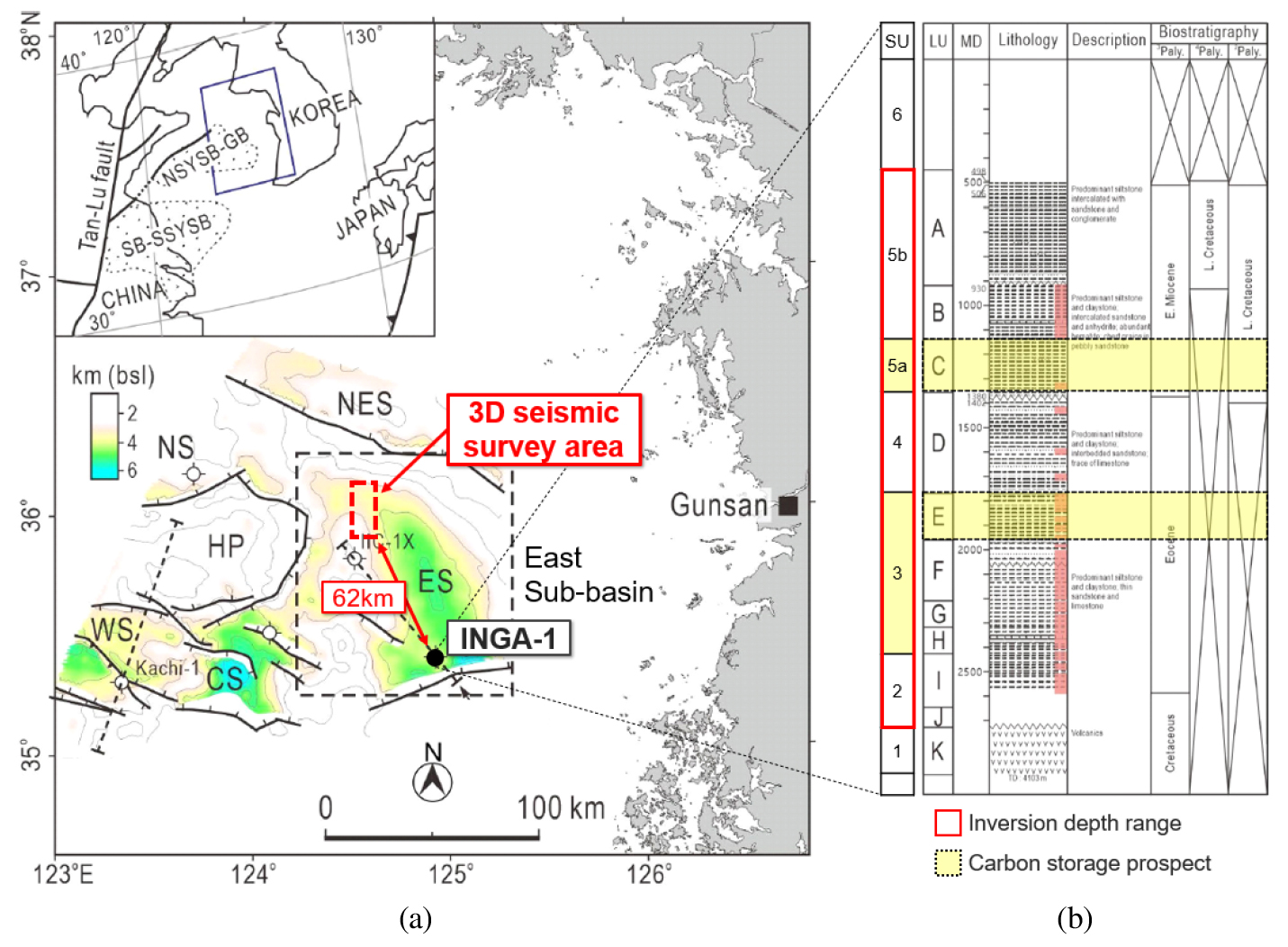
- In this study, we applied prestack impedance inversion to 3D seismic data from the Gunsan Basin, to quantify elastic properties for a …
이 연구에서는 CCS 후보지의 물성을 정량적으로 추정하고자 서해 군산분지에서 취득된 3D 탄성파 자료에 중합전 임피던스 역산을 적용하였다. 탐사지역 시추공 부재로 동일 분지의 …
- In this study, we applied prestack impedance inversion to 3D seismic data from the Gunsan Basin, to quantify elastic properties for a potential CO₂ geological storage site. Because no wells exist in the survey area, low-frequency models for simultaneous inversion were built using logs from a distant well in the same basin. Density logs distorted by borehole washout were corrected using an apparent geometric factor derived from the caliper–density relationship. With the corrected logs, we first performed post-stack impedance inversion to estimate P-impedance and to construct a low-frequency model, and then conducted stepwise prestack inversion to obtain P-impedance, S-impedance, density, and Vp/Vs. The inverted properties show coherent trends within stratigraphic units and Vp/Vs variations linked to lithofacies changes. Prestack inversion results delineate faults and discontinuities clearly, supporting structural interpretation and facies assessment. In future, this workflow can be applied to estimate storage capacity and determine injection well locations in regions lacking wells.
- COLLAPSE
이 연구에서는 CCS 후보지의 물성을 정량적으로 추정하고자 서해 군산분지에서 취득된 3D 탄성파 자료에 중합전 임피던스 역산을 적용하였다. 탐사지역 시추공 부재로 동일 분지의 원거리 시추공을 활용하였으며, 공벽 확장으로 왜곡된 밀도검층은 공경–밀도 관계 기반의 겉보기 거리계수로 보정하였다. 보정 자료를 기반으로 중합후 역산을 선행해 P파 임피던스를 추정하고 이를 저주파수 모델로 구축한 뒤, 중합전 역산을 단계적으로 수행하여 P파 임피던스, S파 임피던스, 밀도 및 속도비(Vp/Vs)를 도출하였다. 그 결과 동일 층서 내 물성의 일관된 경향성과 암상 변화에 따른 속도비의 변화가 확인되었고, 단층·불연속면을 명확히 반영하여 지하 구조 해석 및 암상 분포 평가에 유효함을 보였다. 향후 이 연구에서 제시한 공정은 시추공이 부재한 저장후보지의 저장용량 산정과 주입정 위치 결정에 활용될 수 있다.
-
A Prestack Impedance Inversion for CCS Candidate Site Without a Well: A Case Study of Gunsan Basin
-
Research Article
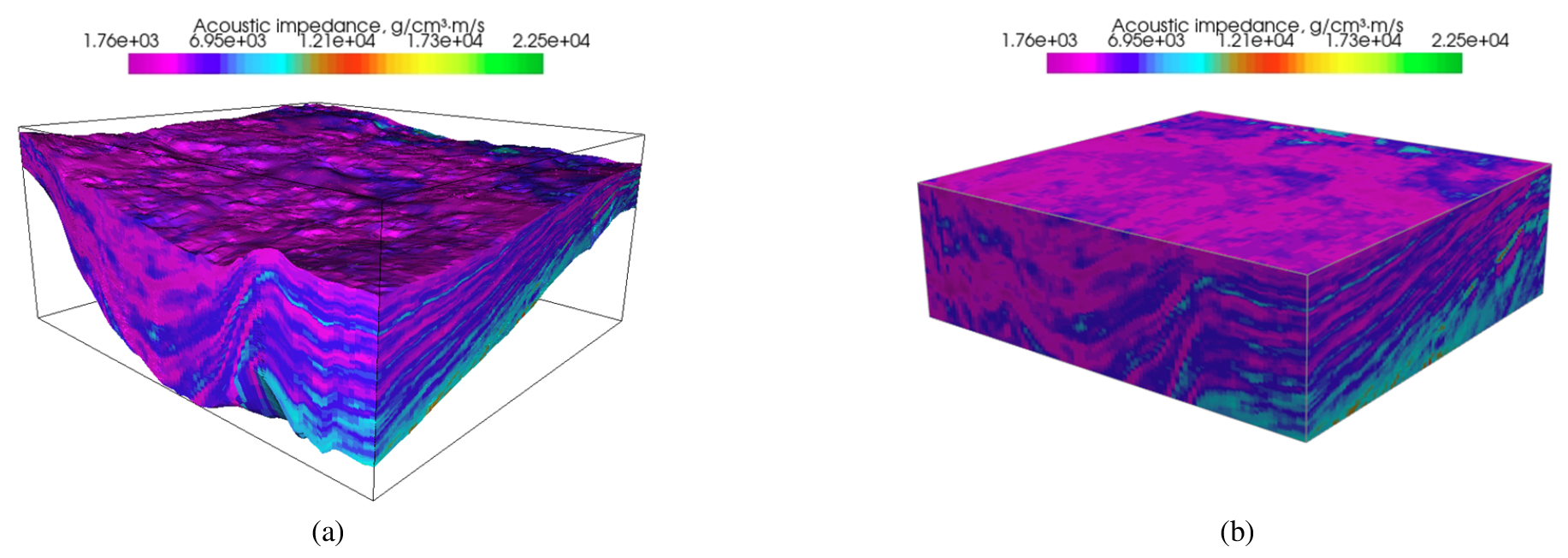
-
Assessment of Facies and Porosity Uncertainty in a West Sea CO2 Storage Reservoir Using 3D Seismic–Driven Geostatistical Ensemble Modeling Techniques
3차원 탄성파 자료와 지구통계 앙상블 모델링을 이용한 서해 이산화탄소 저장소 암상·공극률 모델 및 불확실성 평가
-
Sangin Cho, Hyunmin Kim, Eunsil Park, Jwagyum Kim, Honggeun Jo, Joongmoo Byun, and Sukjoon Pyun
조상인, 김현민, 박은실, 김좌겸, 조홍근, 변중무, 편석준
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is one of the key technologies for achieving carbon neutrality. It serves as a transitional strategy to …
이산화탄소 포집 및 저장(Carbon Capture and Storage, CCS)은 탄소중립 달성을 위한 핵심 기술 중 하나로, 화석연료 중심의 현 산업체계에서 발생하는 탄소배출을 구조적으로 …
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is one of the key technologies for achieving carbon neutrality. It serves as a transitional strategy to systematically reduce carbon emissions from the existing fossil fuel-based industrial system. In particular, the geological storage of carbon dioxide constitutes a critical component for achieving large-scale carbon reduction; this requires a quantitative evaluation of the spatial distribution of reservoir properties and their inherent uncertainties. In this study, we evaluated the distribution and associated uncertainty of reservoir properties within the Early Miocene stratigraphic unit SU5, a proposed prospective CO2 storage formation, using three-dimensional seismic data acquired from the western offshore region of the Korean Peninsula. Acoustic impedance derived from seismic data was utilized to construct geostatistical models of the spatial distribution of rock facies and porosity, and a probabilistic framework was implemented to account for the limited availability of well data. In addition, an ensemble of models incorporating variations in key geostatistical parameters was generated to evalute the spatial variability of reservoir properties. This approach aimed to derive more robust and reliable reservoir property models than those obtained using a single deterministic approach.
- COLLAPSE
이산화탄소 포집 및 저장(Carbon Capture and Storage, CCS)은 탄소중립 달성을 위한 핵심 기술 중 하나로, 화석연료 중심의 현 산업체계에서 발생하는 탄소배출을 구조적으로 저감하기 위한 전환 기술이다. 특히 이산화탄소 지중 저장은 대규모 탄소 감축을 실현하기 위한 필수적인 기술 요소로서, 저장소 물성의 공간적 분포와 이에 수반되는 불확실성에 대한 정량적 평가가 요구된다. 본 연구에서는 한반도 서해권역에서 취득된 3차원 탄성파 탐사 자료를 활용하여, 이산화탄소 저장 유망층으로 제안된 전기 마이오세 퇴적층(SU5)의 저장소 물성 분포와 불확실성을 평가하였다. 탄성파 자료로부터 도출한 음향임피던스(acoustic impedance)를 기반으로 암상 및 공극률의 공간 분포를 지구통계학적으로 모델링하였으며, 시추공 자료가 제한적인 조건을 고려하여 확률론적 접근을 적용하였다. 또한 주요 지구통계 인자의 변동성을 반영한 모델 앙상블 구축을 통해 저장소 물성의 공간적 변동 특성을 분석하고, 이를 통해 단일 결정론적 모델보다 신뢰성 있는 저장소 물성 모델을 도출하고자 하였다.
-
Assessment of Facies and Porosity Uncertainty in a West Sea CO2 Storage Reservoir Using 3D Seismic–Driven Geostatistical Ensemble Modeling Techniques
-
Correction
-
Correction to Application of 3D Printing for Porous Models Simulation in Seismic Physical Modeling
Correction to 탄성파 축소모형 실험에서 다공성 모델 모사를 위한 3D 프린팅 적용성 연구
-
Daechul Kim, Wookeen Chung, and Sungryul Shin
김대철, 정우근, 신성렬
-
Correction to Application of 3D Printing for Porous Models Simulation in Seismic Physical Modeling
-
Correction
-
Correction to Common-Mode Noise Attenuation for Distributed Acoustic Sensing Data
Correction to 분포형 음향 계측 자료의 공통모드 잡음 제거 연구
-
Yongbum Kwon, Woodon Jeong, Kwon Gyu Park, and Changhyun Lee
권용범, 정우돈, 박권규, 이창현
-
Correction to Common-Mode Noise Attenuation for Distributed Acoustic Sensing Data
Journal Informaiton
 Geophysics and Geophysical Exploration
Geophysics and Geophysical Exploration
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Geophysics and Geophysical Exploration
Geophysics and Geophysical Exploration










