-
-
3D Electrical Resistivity Tomography via Horizontal Electric Field Component
3차원 전기비저항탐사 향상을 위한 수평 전기장 성분 측정법 제안
-
Churl Hyun Jo, In-Ki Cho
조철현, 조인기
- Electrical resistivity surveys are one of the most widely used high-resolution near-surface geophysical techniques. However, conventional data acquisition methods based on collinear …
전기비저항탐사는 광물탐사, 토목 및 환경분야 조사 등 천부지구물리탐사 기법중 가장 널리 활용되는 방법으로 주로 공선형배열(collinear array)을 채택하여 수행된다. 이러한 전통적인 현장 자료취득은 …
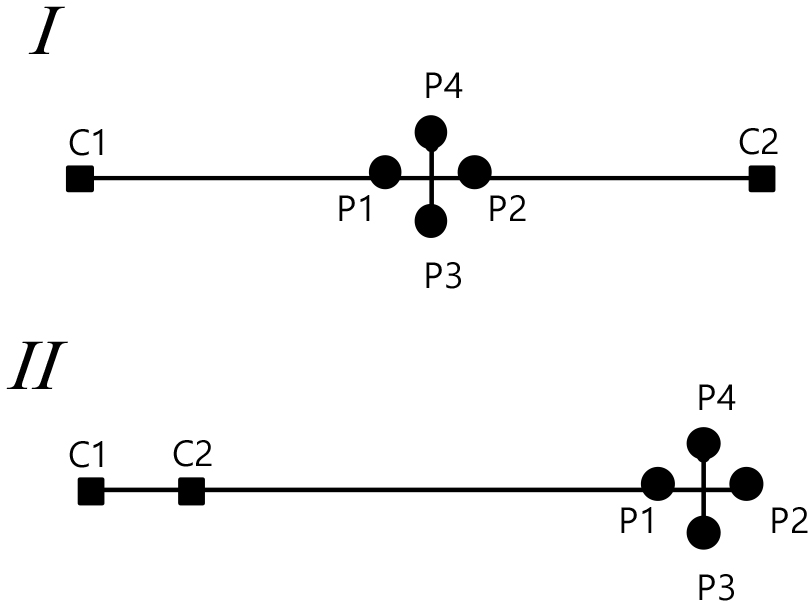
- Electrical resistivity surveys are one of the most widely used high-resolution near-surface geophysical techniques. However, conventional data acquisition methods based on collinear arrays typically measure and interpret only the electric field components aligned with the survey line. Therefore, the horizontal variations in other directions are neglected. Such a limitation is inherent in two-dimensional electrical resistivity tomography (2D ERT); however, it is a critical constraint in three-dimensional electrical resistivity tomography (3D ERT). Hence, this study proposes a method for the vectorial measurement of the horizontal components of electric field changes at potential electrode stations. This approach enables the determination of both the magnitude and direction of surface electric field variation. The resulting data are expected to improve the resolution and reliability of 3D ERT inversion.
- COLLAPSE
전기비저항탐사는 광물탐사, 토목 및 환경분야 조사 등 천부지구물리탐사 기법중 가장 널리 활용되는 방법으로 주로 공선형배열(collinear array)을 채택하여 수행된다. 이러한 전통적인 현장 자료취득은 전기장의 측선방향성분만을 측정하고 해석하고 있다. 이러한 한계는 2차원 전기비저항탐사(2D ERT)에서는 불가피하지만, 3차원 전기비저항탐사(3D ERT)에서는 중요한 제약으로 작용할 수 있다. 본 연구에서는 전위전극 지점에서 전기장 수평성분을 벡터측정하고 해석하는 방법을 제안한다. 이를 통해 지표전기장 변화의 크기뿐 아니라 방향도 함께 파악할 수 있다. 이와 같은 새로운 측정방식은 3D ERT 역산결과를 향상시킬 것으로 기대한다.
-
3D Electrical Resistivity Tomography via Horizontal Electric Field Component
-
-
Resistivity Imaging at the End of a Survey Line using Boreholes
시추공을 이용한 측선 양단 전기비저항 영상화
-
Hwan-Ho Yong, Bongkuk Lee, Gyusang Lee, Jintaek Lim, Hyoung Won, Changkil Eom, In-Ky Cho
용환호, 이봉국, 이규상, 임진택, 원형, 엄창길, 조인기
- Two-dimensional electrical resistivity surveys have difficulty in identifying the electrical resistivity distribution at both ends of the survey line due to insufficient …
2차원 전기비저항 탐사는 가탐 영역의 한계로 측선 양단의 전기비저항 분포를 파악하기 어렵다. 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해서는 측선의 길이를 연장해야 하지만, 현장 여건상 …
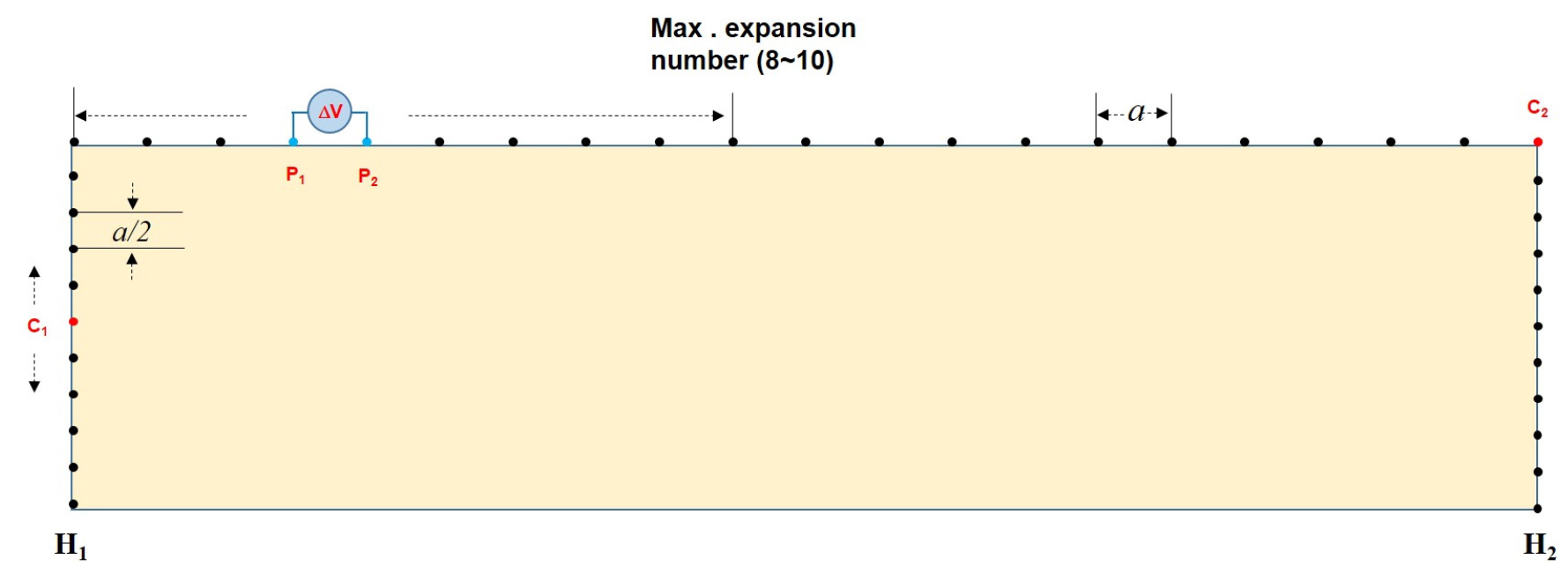
- Two-dimensional electrical resistivity surveys have difficulty in identifying the electrical resistivity distribution at both ends of the survey line due to insufficient data coverage. To overcome this limitation, the length of the survey line must be extended. However, depending on the field situation, it is often not permitted to extend the survey line. This study proposes a method to effectively image the electrical resistivity at both ends of the survey line by combining surface and borehole surveys to overcome this problem. The effectiveness of the proposed method was analyzed through numerical experiments, and its applicability was examined through inversion of field data.
- COLLAPSE
2차원 전기비저항 탐사는 가탐 영역의 한계로 측선 양단의 전기비저항 분포를 파악하기 어렵다. 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해서는 측선의 길이를 연장해야 하지만, 현장 여건상 측선 연장이 불가능한 경우가 빈번하다. 이 연구에서는 이러한 문제점을 극복하기 위하여 지표 탐사와 시추공 탐사를 병행하는 방법을 통하여 효과적으로 측선 양단 하부의 전기비저항 영상화 방법을 제시하였다. 수치실험을 통하여 제시된 방법의 효과를 분석하였으며, 현장 자료의 역산을 통하여 그 적용성을 검토하였다.
-
Resistivity Imaging at the End of a Survey Line using Boreholes
-
-
Application of Induced Polarization Survey in Active Fault Investigation
활성단층조사에서 유도분극탐사 활용
-
Samgyu Park
박삼규
- This study aims to address the limitation of electrical resistivity surveys in distinguishing between weathered and altered zones and fault damage zones …
본 연구는 피복된 활성단층 조사에서 전기비저항 탐사만으로는 풍화 및 변질대와 단층 파쇄대를 명확히 구분하기 어려운 한계를 보완하기 위해 유도분극(IP, Induced Polarization) 탐사 …
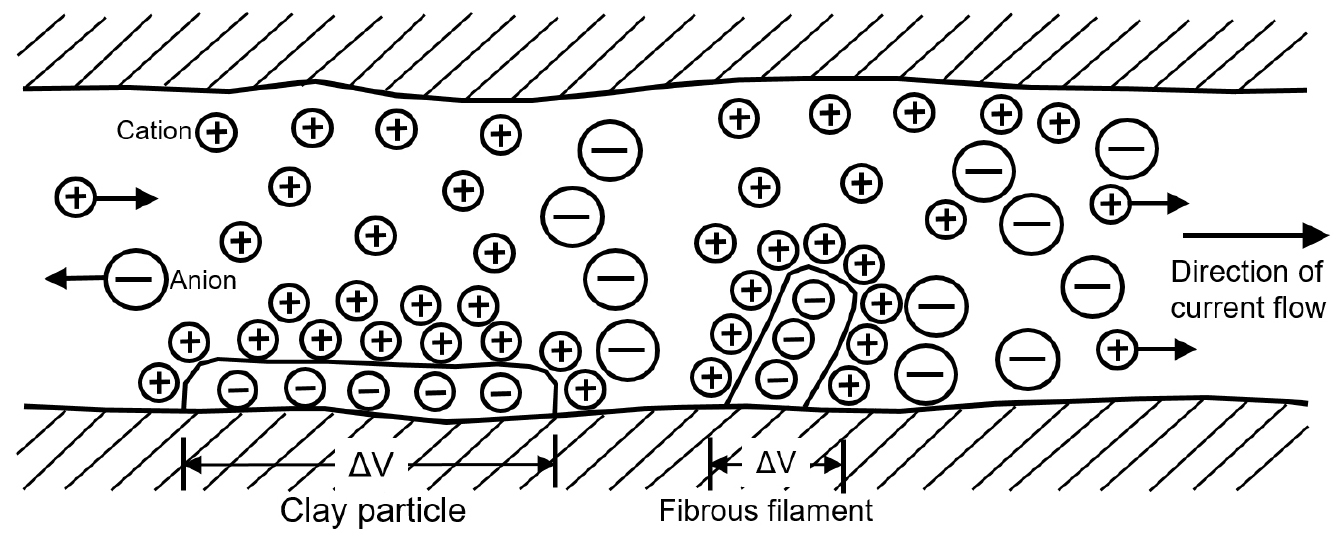
- This study aims to address the limitation of electrical resistivity surveys in distinguishing between weathered and altered zones and fault damage zones when investigating buried active faults. To overcome this, induced polarization (IP) surveys were conducted in parallel with resistivity measurements, and the effects of electrode type on chargeability response were analyzed. The study site is located in the Miho area of the southern Yangsan Fault, where a previously conducted trench investigation confirmed the presence of fault gouge. IP data were acquired using both stainless steel and non-polarizable electrodes as potential electrodes, and the resulting chargeability distributions were compared. Both methods revealed high chargeability responses in the fault gouge zone between 13 m and 20 m along the survey line. The use of non-polarizable electrodes resulted in broader and clearer high-chargeability zones, indicating superior signal fidelity. However, the stainless steel electrodes also yielded meaningful results in areas where strong polarization responses were present, offering the advantage of field efficiency. This study demonstrates that combining electrical resistivity and IP surveys enhances the reliability of fault zone interpretation and that chargeability distribution can serve as an effective supplementary tool for identifying buried active faults when used in conjunction with trench investigations.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 피복된 활성단층 조사에서 전기비저항 탐사만으로는 풍화 및 변질대와 단층 파쇄대를 명확히 구분하기 어려운 한계를 보완하기 위해 유도분극(IP, Induced Polarization) 탐사 기법을 병행하여 적용하고, 전극 종류에 따른 충전율 반응 특성을 비교 분석하였다. 연구 대상지는 남부 양산단층에 위치한 미호리 지역으로, 기존 트렌치 조사에서 단층비지가 확인된 구간을 중심으로 전기비저항 및 IP 탐사를 수행하였다. IP 탐사에서는 전위 전극으로 스테인리스 전극과 비분극 전극을 각각 사용하였으며, 두 방식으로 획득한 충전율 분포를 비교하였다. 그 결과, 측선 거리 13~20 m 구간의 단층비지 분포 영역에서 두 방식 모두 고충전율 반응이 나타났으며, 비분극 전극을 사용한 경우 충전율 분포가 보다 넓고 명확하게 나타났다. 반면, 스테인리스 전극을 사용할 경우에도 단층비지의 분극 반응이 강할 때는 유의미한 해석이 가능하였으며, 현장 작업의 효율성 측면에서 장점을 가질 수 있음을 확인하였다. 본 연구는 전기비저항 탐사와 IP 탐사를 병행하여 해석할 경우 단층 파쇄대의 해석 신뢰도를 향상시킬 수 있으며, 충전율 분포는 트렌치 조사와 연계하여 피복된 활성단층 탐지에 효과적인 보조 자료로 활용될 수 있음을 제시한다.
-
Application of Induced Polarization Survey in Active Fault Investigation
Journal Informaiton
 Geophysics and Geophysical Exploration
Geophysics and Geophysical Exploration
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Geophysics and Geophysical Exploration
Geophysics and Geophysical Exploration










